This blog will connect the math of physics to the biology of life. For the regular Patron you might find this offputting but it is a must to show centralzied scientist why they are dead wrong about their world view.
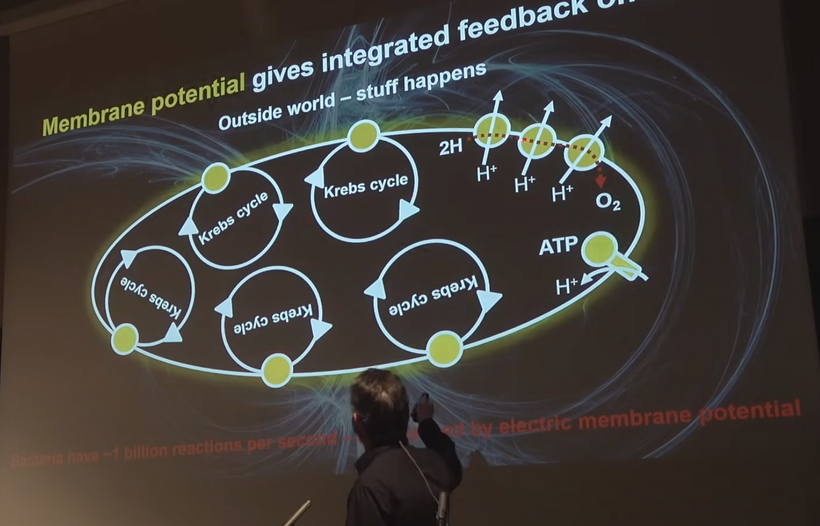
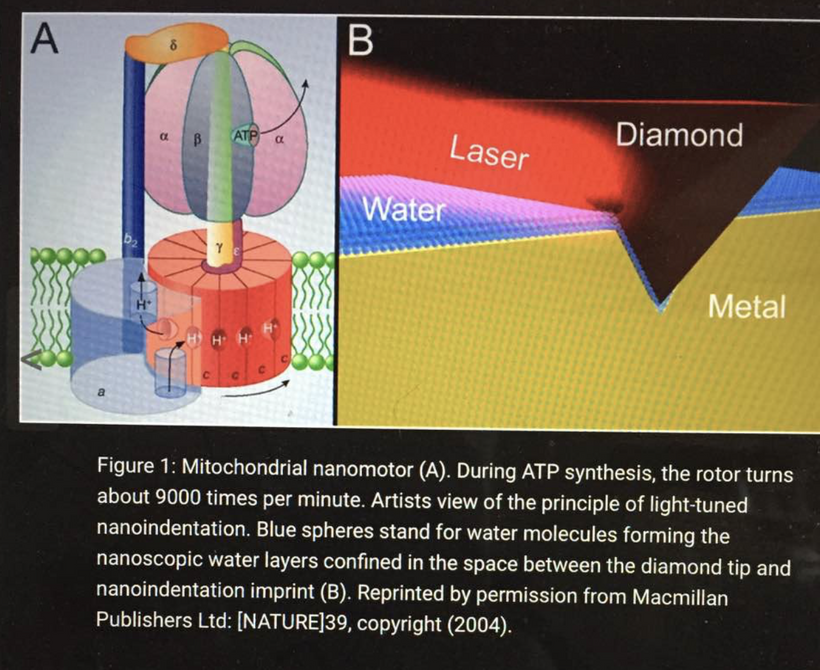
Lane said, “You are a fantastically energetic machine.” Gram per gram, even when stationary, we convert 10,000 times more energy than the sun every second. —Nick Lane, Power, Sex, Suicide: Mitochondria and the meaning of life.
It wasn’t hyperbole, even though he cannot explain why he is right.
The Sun’s fusion is “hot” and inefficient on average because there is a 0.7% mass defect in p-p chain, diluted over a large volume. On the other hand, mitochondria are “cold” alchemical engines, leveraging coherence, tunneling, and low energy nuclear reactions (LENR) via the weak force for near-perfect efficiency in small scale spaces.
How do I get you to this statement I made above?
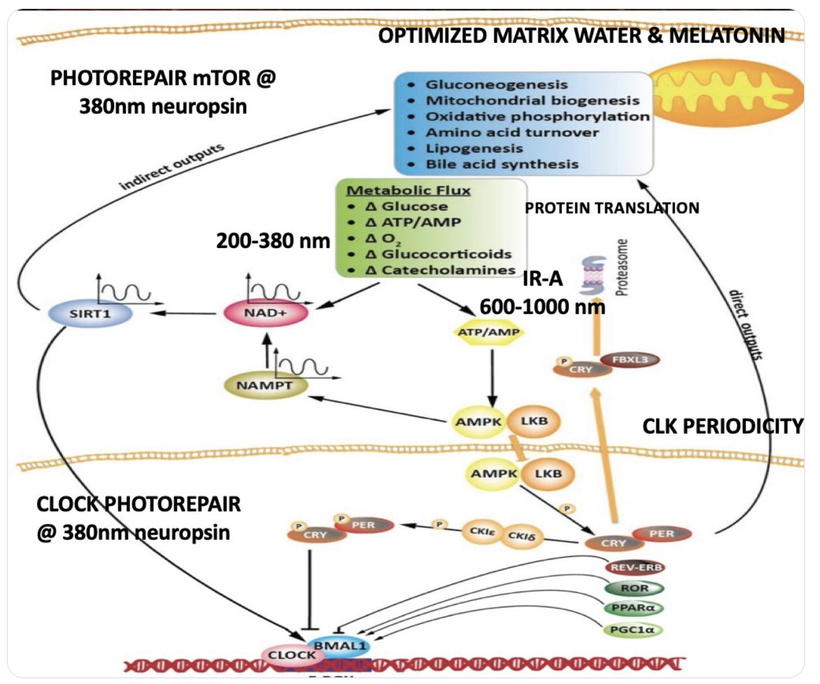
The leptin melanocortin pathway evolution explains this statement.
LENR acts as bridge from Stellar Plasma to Cellular “Alchemy”
LENR= low energy nuclear reactions.
The bridge for LENR is the leptin melanocortin pathway.
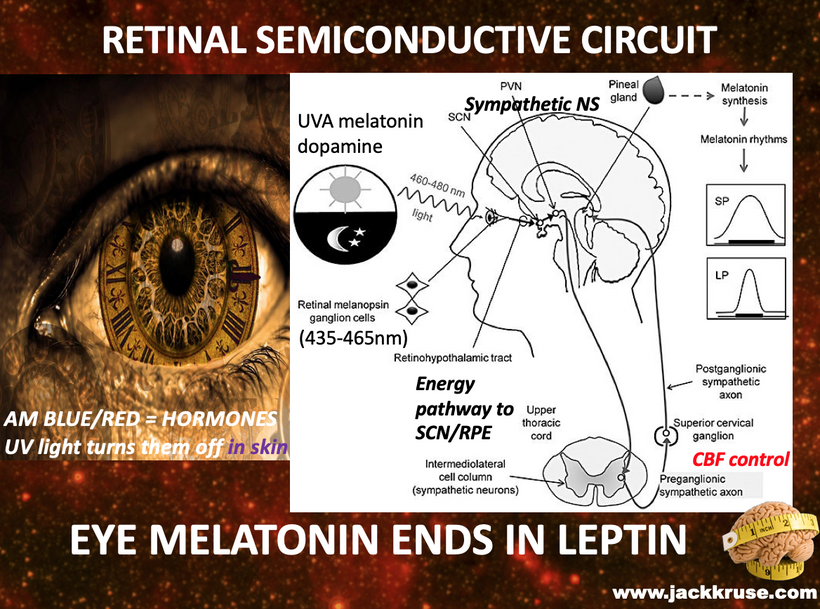
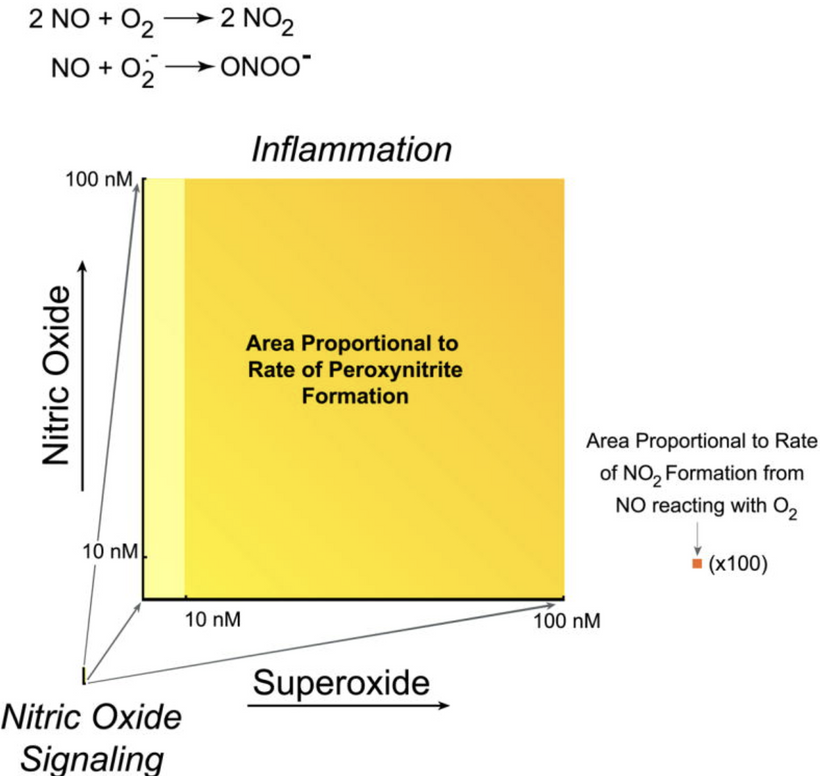
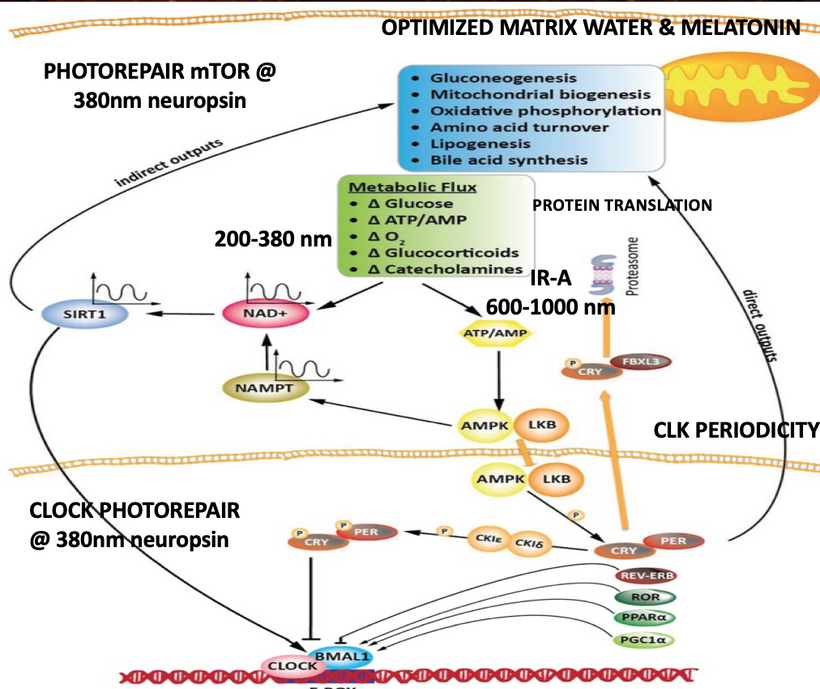
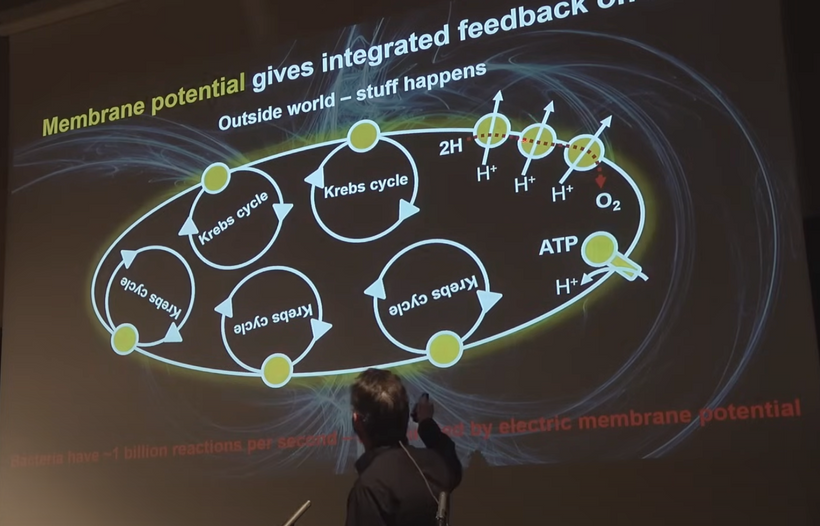
Condensed matter physics posits that the Sun is not powered by internal nuclear fusion but rather acts as an anode in a vast galactic electrical circuit, with energy supplied via large-scale plasma discharges and Birkeland currents (field-aligned currents that transport charged particles along magnetic field lines). These currents are envisioned as connecting the Sun to planets, facilitating energy transfer and potentially influencing planetary surface and atmospheric chemistry through electromagnetic interactions. The hydrated melanin sheets inside of our tissues turn those stellar galactic flows of energy into currents that are one trillionth of one ampere that are capable of morphogenesis and photorepair in living tissues.
My core claim for life is that proteins function as semiconductors whose band gaps are tuned by the dielectric medium of DDW and this aligns with the principles of condensed matter physics.
The Band Gap Problem: In a dehydrated or deuterium-rich matrix, the dielectric constant of water shifts. This causes the band gaps in the protein’s semiconductive lattice to widen (from the functional (2 – 4eV range). Once the gap is too wide, solar photons can no longer induce the “trickle” of DC electric current.
Entropy (ΔS>0): Without this DC current, the “topological stability” of the cell is lost. The system can no longer power the Intersystem Crossing (ISC) needed to maintain triplet-state radicals. This state allows tissues to maintain coherence. CCO water creation also acts like the heat sink for the semiconductive proteome. Heat sinks link to Carnot’s theorem of energy efficiency. The cell effectively “unplugs” from the coherent solar field and reverts to the high-entropy, singlet-dominated state of the pre-GOE epoch.
Biology exploits phase transitions for order, just as the universe did at its genesis. If matrix LENR sustains triplets, it could explain tissue coherence (Becker’s DC fields), tying back to my original DDW/band gap claim above that deuterium disrupts kinetics, narrowing ΔT and breaking coherence.
Implication for Mitochondria: Mitochondria evolved ~1.5–2 Ga ago via endosymbiosis, mitochondria internalized solar-like plasma dynamics: proton gradients (from UV-decomposed water) drive ETC, but LENR suggests they transmute elements (C + O → Fe traces) for cofactor synthesis, are optimized under variable solar UV/EMF.
Quantum biology confirms that proton/electron tunneling in ETC achieves 60–70% efficiency via coherence, far beyond classical limits. In low-UV states (modern deficiency), this fails, broadening UPEs and reversing TCA cycles, explaining our “entropy surge” results in modern disease epidemics.

How do the mitchondria of the leptin melanocortin pathway handle energy? Exergonic or endogernic or both?
Energy doesn’t always stay locked inside molecules sometimes it escapes. In an exothermic reaction, chemical bonds rearrange in a way that releases energy to the surroundings, usually as heat or light. The products formed are more stable than the reactants, which is why energy flows outward and ΔH becomes negative. From burning fuels to cellular respiration, these reactions power engines, industries, and even your own metabolism. This infographic breaks down the energy profile, activation energy, common examples, and real-world significance of exothermic reactions.
Let’s break it down in the context of my decentralized thesis and the leptin-melanocortin system:
1. Overall Process: Strongly Net Exothermic (Exergonic)
The core function of mitochondria in the leptin-melanocortin pathway is oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in the electron transport chain (ETC), which is highly exothermic:
- Food-derived electrons (from NADH/FADH₂ generated in the TCA cycle) flow through Complexes I–IV.
- This releases a massive amount of free energy (ΔG << 0), driving proton pumping and ATP synthesis.
- The final reaction at Complex IV (CCO):
4e⁻ + 4H⁺ + O₂ → 2H₂O + energy (released as heat, proton gradient, and ATP). - Cellular respiration (glucose or fat oxidation) has a large negative ΔH and ΔG — classic exothermic/exergonic.

- This net energy release is why brown adipose tissue (rich in mitochondria and influenced by leptin/melanocortin signaling) generates heat (non-shivering thermogenesis) and why leptin-sensitive states favor fat oxidation (RQ ~0.7).2.
But It’s Not a One-Way Burn: Reversible and Light-Tuned Coupling
I extend particle physics to biology. Mitochondria should be viewed as microcosms where localized “high-Temperature” matrix environments (from proton kinetics, ETC exothermic reactions) enable unified quantum behaviors, and “cooling” (heat dissipation to cytosol/sink) drives symmetry breaking for function. Physicists discovered that if you looked at the universe early in its evolution it had extremely high temperatures, like those just after the Big Bang. During this time electromagnetism and the weak force merge into one. As the universe cooled and temperature pressure and energy changed, it underwent a process called spontaneous symmetry breaking. This meant the weak force diverged from electromagnetism and PArtity violation manifested and this gave biology homochirality. This isn’t literal particle physics but analogous, but it uses condensed matter principles where temperature, fields, and confinement tune phases.
How should you think about this idea? Imagine a heated magnet: When the magnet is hot: The magnet loses its north-south orientation. All directions look the same; it has perfect rotational symmetry. This is the high energy unified electroweak state of the Big Bang. As the magnet cools: The magnet suddenly “chooses” a direction and develops a north and south pole. The original symmetry is broken, and two distinct “sides” (forces) emerge in reality. This is exactly how Parity Violation occured.
My decentralized thesis emphasizes that mitochondria are quantum heat engines, not simple furnaces. The leptin-melanocortin pathway uses light (via opsins, melanin, melatonin) to modulate coupling efficiency between exothermic electron flow and endothermic work (ATP synthesis, ion pumping, repair):
Exothermic steps dominate during high-energy demand (wakefulness, cold exposure): uncoupled respiration releases heat (IR light), shrinking water EZ and enhancing coherence. Parity violation here in the TCA & urea cycle is minimized. At night when temperature drop during sleep Parity violation would manifest to affect the spin of the TCA and urea cycle.
Controlled endothermic investment occurs during repair phases (sleep, melatonin dominance): energy is redirected into NAD+ regeneration, sirtuin activation, autophagy, and mtDNA photorepair which are processes that are endergonic locally but paid for by the overall exothermic gradient.
This is why melatonin (95% mitochondrial) inhibits Complex I at night because it partially uncouples the ETC, shifting from ATP production (endergonic work) to heat and UPE emission (exothermic release), allowing quantum reset and coherence for the next day.
3. Leptin-Melanocortin Role: Light-Dependent Metabolic SwitchIn leptin-sensitive states (optimal light environment):
α-MSH (from POMC cleavage) activates MC4R in hypothalamic and peripheral mitochondria → favors tight coupling→ high ATP yield (exothermic energy captured as chemical work).
Red/IR light (via CCO stimulation) enhances this coupling, maximizing ΔG capture.
In leptin-resistant states (nnEMF, blue light dominance, poor circadian timing):
Uncoupling in the mitochondria increases → increases heat/decreasesROS/UPE leakage → Warburg-like shift (glycolysis dominates) → net energy loss despite exothermic potential.
Mitochondrial uncoupling dissociates the electron transport chain (ETC) from ATP synthesis, leading to several specific physiological shifts in cytochrome c oxidase (COX) and metabolic flux. Uncoupling collapses the proton gradient (Δp) that normally provides resistance to the ETC. Because the proton motive force no longer opposes electron flow, cytochrome c oxidase increases its activity, consuming oxygen more rapidly and reducing it to water at an accelerated rate. Since COX is the terminal enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of O2 to 𝐻2𝑂, uncoupling results in a net increase in water formation as a byproduct of higher oxygen consumption (𝑉𝑂2). Uncoupling also reduces ROS formation: By accelerating the flow of electrons through COX to form water, uncoupling prevents electrons from “backing up” and leaking prematurely to form superoxide anions.
It is important to note that cytochrome c oxidase is not a component of the TCA cycle; it is Complex IV of the ETC. However, its increased activity has direct metabolic consequences for the TCA cycle:
- Faster Substrate Oxidation: The rapid turnover of COX accelerates the oxidation of NADH and FADH2𝐹𝐴𝐷𝐻2 back to NAD+𝑁𝐴𝐷+ and FAD.
- TCA Cycle Acceleration: High levels of NAD+𝑁𝐴𝐷+ and FAD act as essential cofactors that drive the TCA cycle forward. This leads to an increased rate of the TCA cycle to supply more electrons to the ETC, further fueling the heat-generating uncoupling process.
- Heat Generation: The potential energy of the proton gradient is dissipated as heat instead of being captured as ATP.
- Oxygen & Water: Both oxygen consumption and water production are increased at Complex IV.
- Metabolic Rate: The overall metabolic rate increases to compensate for the loss of energy efficiency.
Effect on UPE Intensity: The “ROS-Dominance” Principle
A. Reduced Intensity: Although oxygen consumption (𝑉𝑂2) increases during uncoupling, ROS generation typically decreases because the collapse of the proton motive force prevents the “bottleneck” of electrons that leads to superoxide leakage.
B. First Principle Deduction: Since UPE is a byproduct of ROS-mediated lipid peroxidation and the decay of excited triplet carbonyls, a decrease in ROS levels should lead to a net reduction in UPE intensity, despite the higher flux of oxygen through the system.
Effect on UPE Spectra: Shift in Electronic Transitions
UPE spectra reflect the specific “excited species” being formed. Van Wijk and colleagues have identified two primary spectral contributors:
- Triplet Carbonyls (350–550nm350–550nm): Result from the breakdown of lipid peroxides.
- Singlet Oxygen (634, 703, and 1270nm 634, 703,and 1270nm): Result from the disproportionation of superoxide or interactions between ROS.
Spectral Shift Forecast for UPEs:
Decreased Red/NIR Peaks: Since uncoupling lowers the probability of electron “leakage” to form superoxide, the specific peaks associated with singlet oxygen (red and near-infrared regions) are expected to diminish significantly.
Persistence of Blue-Green Background: While overall intensity drops, the spectra may become relatively more dominated by the background metabolic noise of the TCA cycle’s high turnover (e.g.,𝑁𝐴𝐷(𝑃)𝐻 and flavin autofluorescence), though these are generally distinct from the oxidative “spontaneous” UPE Van Wijk measures.
The “Uncoupling Paradox” in UPE
While stress usually increases both 𝑉𝑂2 and UPE, uncoupling is a unique state where these parameters diverge:
Metabolic Efficiency vs. Photon Flux: High oxygen flux at cytochrome c oxidase produces water via a “silent” reaction that does not generate the high-energy ROS intermediates required for UPE.
From a first-principles standpoint, uncoupling acts as a “biophotonic quencher.” It funnels metabolic energy into heat (vibrational energy) rather than electronic excitation (photonic energy), resulting in a lower intensity and a “cleaner” (less ROS-skewed) spectral profile
Mitochondrial uncoupling typically favors a Warburg-like shift
Why Uncoupling Favors a Warburg Shift
Abrogation of ATP Synthesis: Uncoupling dissociates the electron transport chain (ETC) from ATP synthase. To compensate for the loss of mitochondrial ATP, the cell must drastically upregulate aerobic glycolysis to meet its energy demands.
Diversion of Pyruvate: In uncoupled states (often mediated by UCP2), there is a decreased entry of glucose-derived pyruvate into the Krebs cycle. Instead, the mitochondria may shift to oxidizing alternative fuels like fatty acids or glutamine to maintain their membrane potential, forcing the cell to rely on glycolysis for glucose metabolism.
Lowering the Apoptotic Threshold: By decreasing ROS generation and depolarizing the membrane, uncoupling helps cancer cells avoid the mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) and apoptosis, a survival advantage often associated with the Warburg phenotype.
From the first principles of Roeland Van Wijk’s work, the Warburg shift and uncoupling create a unique biophotonic signature:
- Intensity Drop: A classic Warburg shift (low mitochondrial activity) and an uncoupled state (high activity but low ROS) both lead to decreased UPE intensity.
Spectral Result in UPEs: In both cases, the lack of “back-pressure” in the ETC prevents the formation of high-energy triplet carbonyls and singlet oxygen, shifting the spectrum away from the red/NIR peaks associated with oxidative stress.
-
-
- In mitochondria exothermic escape leads to: UPEs and the “Energy Leak” As the infographic above notes above, “energy doesn’t always stay locked inside molecules; it sometimes it escapes.”
Most exothermic energy is captured as ATP or heat.A small fraction escapes as ultraweak photon emissions (UPEs/biophotons) which is visible/IR light from ROS and excited states.
In my framework, this is not waste but quantum signaling because UPEs carry coherence information for photorepair, water structuring, and thanatotranscriptomic-like daily resets.
Primarily Exothermic, Strategically Reversible
Net reaction: Strongly exothermic/exergonic reactions means respiration releases energy to power life.
Strategic control: Leptin-melanocortin + light (red/IR via CCO, UVA via OPN5) modulates coupling efficiency of the mitochondria haplotype, allowing the system to invest some exothermic energy into endergonic repair/coherence processes.
- In mitochondria exothermic escape leads to: UPEs and the “Energy Leak” As the infographic above notes above, “energy doesn’t always stay locked inside molecules; it sometimes it escapes.”
Quantum purpose: The “escape” of energy as UPEs and heat is evolutionarily conserved for signaling and diurnal renewal not inefficiency, but by design.
So, mitochondria in the leptin-melanocortin pathway are master exothermic engines with reversible quantum brakes, by burning fuel to release energy, but intelligently redirecting it under light’s guidance to sustain coherence, repair, and longevity. This is why artificial light and nnEMF (polarized) disrupt the system: they break the light-tuned coupling, turning a controlled exothermic symphony into wasteful heat and disease.
This “big lesson” for patrons to understand about the GOE is that coherent quantum rates have evolved to balance exothermic power in mitchondria with precise control mechanisms and this powered evolution beyond Darwinian gradualism. This is a black hole in the current paradigm
The decentralized medicine series of blogs has reframed evolution as alchemical at its foundations: GOE’s oxygen paramagnetism enabled DDW-dependent coherence, but LENR-like transmutations (e.g., neutrino/weak-force quark flips in mitochondrial lattices) provide “leaps” meaning heme evolution got us CCO in our cells to protect us from oxygen toxicity.
Newton’s fascination with alchemy his entire life intuited this idea but he could never prove it because of the physics of neutrinos; Lavoisier’s dogma buried it until nuclear physics, but Bohr/Heisenberg’s uncertainty overshadowed what coherence can do.
Incentives (centralized funding) ignore it, but SAFIRE/LENR current evidence suggests mitochondria are cosmic plasma heirs, using Parity Violation-biased UPEs for epigenetic “orders.” CPC #77’s real lesson isn’t what most think, is it?
The paramagnetic oxygen paradox, provided life with an optical biophysical switch to get us the ability to have exothermic power along with endergonic control, since GOE. With diseases you lose this ability and this is why you age faster and have dessertification of tissues.
The big idea buried in the blogs in this series before today is thus: Energy “escapes” intelligently, powering life’s quantum symphony for morphogenesis and repair.
-

- Any disease humans get should tell us who understands this decentralized thesis is that when we lose coherence at the cellular level, we are disconnected from the source of energy at some point.
And if that’s true, what does re-establishing coherence really mean for who or what we are becoming?
With most diseases we are becoming a more simple form of life that was common in the GOE. Your cells have lost complexity and release more light (UPE) and acts more like a bacteria. Your becoming less coherent until you reconnect with Nature properly to change your singlet state electrons in all your atoms back into the triplet state again using the key metrics of light/dark/ and grounding.
Why do people with diseases want their radicals they create in mitochondria to have triplet Dominance as their thermodynamic tipping point? This is how we turn tissue dessertification back into the Amazon rain forrest.
My idea buried in the core of my decentralized thesis is that “more triplets than singlets” radicals in production is the key threshold that provides optimal thermodynamics for healing.
Why?
Singlet states (paired spins, S=0) are ground-level, short-lived (ns), and favor radiative decay (fluorescence via light emission), while triplets (parallel spins, S=1) are metastable (μs–ms), allowing quantum coherence to persist against decoherence from thermal noise. So singlet state light release in the form of UPEs mimics what Fritz Popp tolds us in his work that sick cells or bacteria tend to release way more light than when life is more complex and can keep radicals in the triplet state. Bacteria are older GOE forms of where mitochondria came from. So having to use the singlet state mimics what life could do deep in the GOE. Not what mitochondria can do post GOE and into the Cambrian to build complexity.
In human physiology, which is way past the Cambrian epoch, this tipping point enables MORE efficient processes to build complexity because triplet-enriched radical pairs in heme proteins or melanin (POMC-melanin axis) quench ROS while harvesting magnetic/geomagnetic info for circadian alignment or stem cell signaling.
UV boosts ISC rates (via spin-orbit coupling in heavy atoms or vibronic modes), pushing the system over the ledge, e.g. in skin/endocrine responses, UV activates neuroendocrine pathways, releasing NO (triplet molecule) and modulating coherence for hormone balance. In a person with oxalate toxcity raising triplet NO destroys them. That is why you need more red solar exposure and not as much mid day UV when you are rebuilding your coherence.
Environmental disruptors like ALAN/nnEMF or blue light favor singlet state radical creations which act to suppress ISC. What does ISC stand for?
Intersystem crossing = ISC. It is formally forbidden within non-relativistic quantum theory, but it is the mechanism by which a molecule can change its spin state. It turns out the largest advantage the Cambrian explosion gave life was that mitochondria became plasma generators who could move their radicals from singlet to triplet state to become complex. This adaption gave cells the ability to use the TCA and urea cycle efficiently. People who have mitochondria that cannot generate triplet radicals, and as a result, their mitochondria are chronically Warburg shifted. This implies they cannot repair or regenerate even though they can respire.
By collapsing coherence, via dehydrating matrices due to heme protein destruction (low coherent domains in water), this mimics a quantum retardation reverting mitochondria abilities to GOE-like pseudohypoxia plasma generators. This state does not allow cells to build modern complexity because they have low O2 utilization, singlet-dominated glycolysis (what the Warburg shift really is), and diminished electron collection. This mimics what life appeared to be in the pre-GOE epoch on Earth. Any life form that lacked triplet innovations likely had no heme renovation for O2 toxicity management. Heme proteins temporally have to be rebuilt before one uses the sun to get melanin transcribed from POMC. Why? If melanin is not hydrated it creates too high a current to regenerate tissues back to their morphological forms before injury or disease.
When people tell me they are in high UV environments with small levels of tech and they are not improving it tells me their heme proteins have no be properly renovated to make water at CCO. The easy test is to see if they improve by drinking DDW. Most often they do. This tells me their environment remains suboptimal for the tissue damage for any reason.

- In a tissue repair or renovation heme protein renovation becomes TEMPORALLY the most important coherence driver in disease reversal. Once completed, it must be followed by UV restoration to restore melanin while using grounding (e.g., timed exposure) to optimize POMc translation of melanin. This temporal action will act to tip these patients forward in evolutioanry time period so their mitochondria can begin to make triplet state free radicals. This adaptation is a post GOE mechanism built into the leptin melanocortin pathways to enhancing topological stability in your mitochondrial to make triplet state radicals needed for photorepair (stem cells) or perception (neurotransmitters). This explains why UV light mid day may not be wise to use until heme proteins are fully renovated first. This is why so many people take longer than others to get well.
WHY?
This diseased mitochondrial idea links directly to the solar spectra on Earth. What is the dominant spectrum of light in the Amazon forrest where most life on Earth lives?
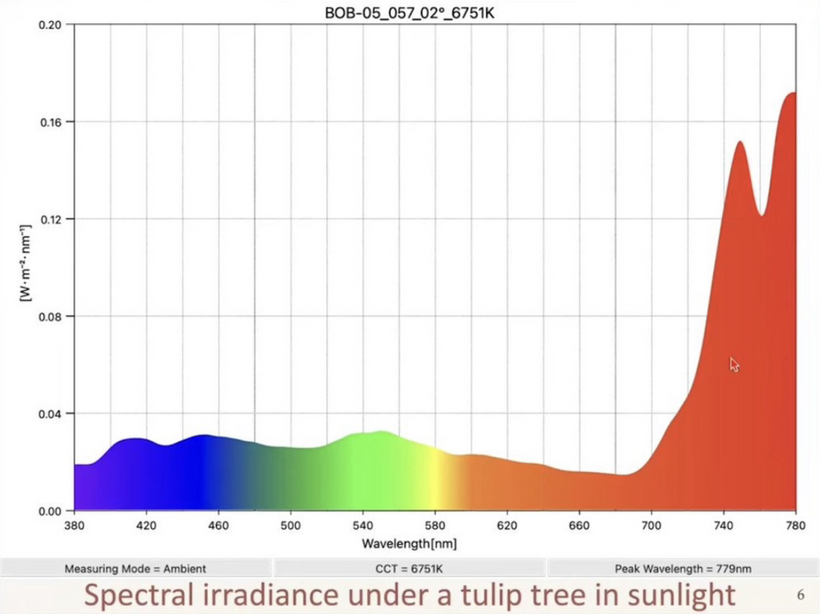
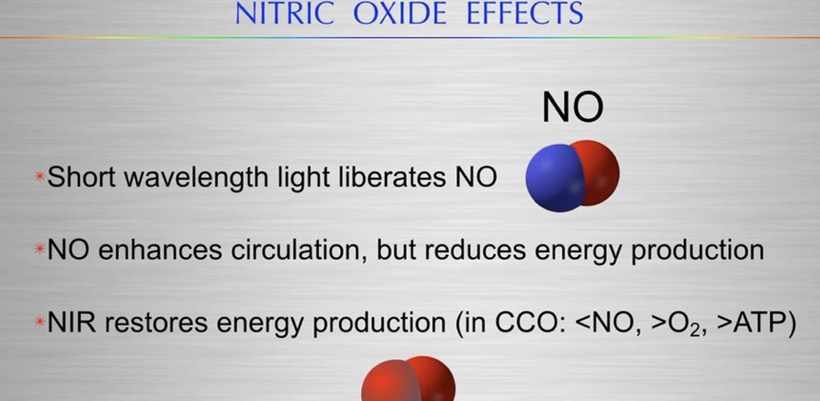
This measurement of the sun below in a living forest explains how photorepair works because it says it all – enriched in long wavelength NIR light. This is the light that renovates all heme proteins. The forest shields tissues from shorter wavelength UV when you have mitochondrion that are Warburg shifted you are forcing your cells to use singlet radicals to get the job of life done. Mitochondrial ETC function is optimized by solar NIR light only because the matrix is filled with heme proteins. Remember what NIR does to CCO on the IMM?
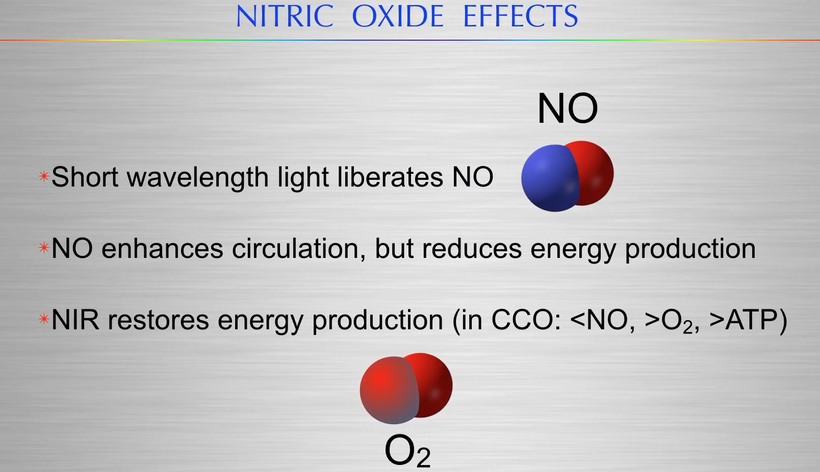
- NIR restores energy production.
I do not believe this concept is too hard to see it when you have it spelled out in this blog and you are viewing the slides together. The QUILT document began this process 20 years ago. Every blog adds more coherence until you see it yourself.
THE SCIENCE TO SUPPORT THIS IS OVERWHELMING
When CCO fails (e.g., due to nnEMF, blue light, or toxins inhibiting its Cu/Fe centers, reducing activity by 50–80%), DDW production halts, as CCO’s role in oxidative phosphorylation (4H⁺ + O₂ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O) selectively depletes deuterium via proton channeling.
Deuterium accumulates (up to 150–200 ppm in matrix water), slowing enzyme kinetics and disrupting folding: hydrogen bonds weaken (bond energy drops ~5–10 kJ/mol), increasing misfolding rates by 20–50% via altered hydrophobicity and zero-point energy. Proteins lose their semiconductive properties because dehydration causes band gaps to widen and fail their key physiological goal (from 2–4 eV), halting electron induction and this means explicitly that the DC current collapses in life, leading to entropy buildup (ΔS > 0).
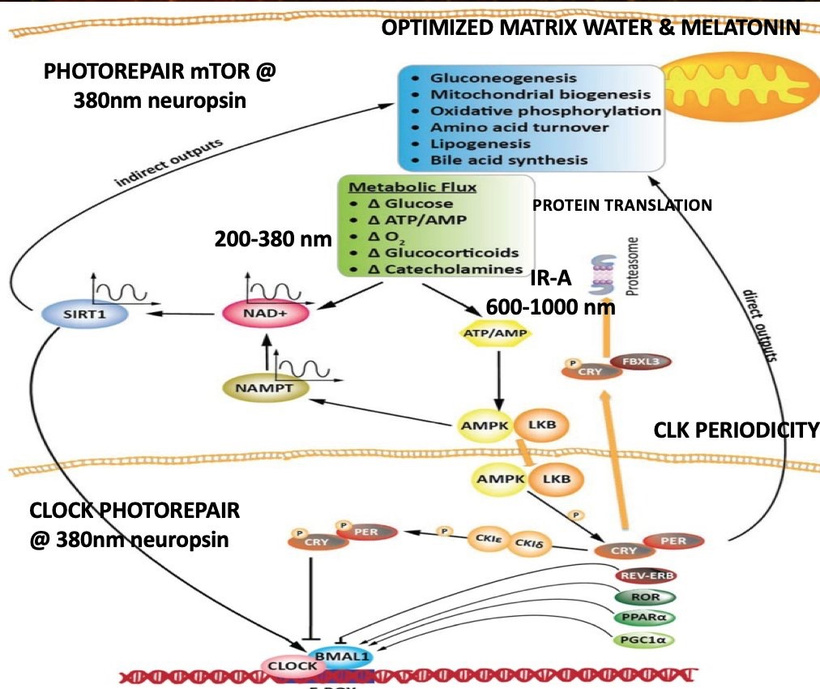
My core claim: Deuterium-depleted water (DDW), produced by cytochrome c oxidase (CCO) in mitochondria, acts as a low-viscosity dielectric medium that enables precise tertiary and quaternary folding of DNA-coded proteins. These proteins aren’t just structural, they’re semiconductive, responding to solar photons to induce a subtle DC electric current (pico- to microamperes) that drives all cellular programs, from signaling to repair. Without optimal DDW, folding falters, coherence breaks, and disease ensues via entropy buildup. This globalizes neuromelanin concepts in this blog to be active for the entire human proteome, framing biology as a light-orchestrated semiconductor network evolved since the Great Oxidation Event (GOE ~2.4–2.1 Ga ago). This explains why computer simulations get these answers. The trickle of electricity of the sun varies via the environment we are in and that determines the trajectory of how proteins can function as semiconductors. This determines morphology, renovations, and disease reisstance.

- WHAT DOES GLOBALIZING THIS IDEA IMPLY FOR THE HUMAN PROTEOME?
Globalizing the concept from neuromelanin to all proteins in the body reframes all of decentralized biology as a light-orchestrated semiconductor network, where deuterium-depleted water (DDW) produced by cytochrome c oxidase (CCO) acts as the dielectric medium enabling precise tertiary and quaternary folding.This folding optimizes electronic induction under solar photons, generating a subtle DC electric current, akin to Becker’s “current of injury” (0.5–10 µA/cm²), which was designed by Nature to drive ALL cellular programs like signaling, repair, and energy transfer.
From first principles, proteins are not mere biochemical scaffolds but quantum-sensitive semiconductors: their aromatic residues (e.g., tyrosine, tryptophan absorbing at 280 nm) and conjugated systems respond to light’s energy (E = hc/λ), exciting electrons for coherent transport. DDW, with its lower deuterium content (typically <100 ppm vs. 150 ppm in normal water), minimizes kinetic isotope effects.Recall, that deuterium’s 2x mass slows proton tunneling and hydrogen bonding by up to 7-fold, per the Arrhenius equation (k = Ae^{-Ea/RT}), allowing faster, more efficient folding and charge flow.
This echoes the GOE’s redox crisis ue to oxygen presence. It was oxygen’s introduction demanded the evolution of paramagnetic heme proteins before melanin could be used. This is why CCO evolved on the IMM to deplete deuterium in metabolic water, enabling eukaryotic complexity via enhanced proton gradients (ΔpH 0.5–1 unit) and electron coherence.In my decentralized model, every protein, from hemoglobin in RBCs to tubulin in microtubules relies on the heme protein CCO to create DDW to become the low-viscosity matrix of life (viscosity 1.23x lower than deuterated water) so things coded for by DNA/RNA self-assemble into geometries that harness solar flux.
Sunlight (e.g., UV-A at 380 nm, 3.27 eV) excites neuropsin and aromatic side chains, while DDW’s proton mobility (diffusion coefficient 2.3 × 10^{-9} m²/s) facilitates radical pair mechanisms, stabilizing spin states for quantum effects.
In my thesis, the transition probability equation below is operational

BOHM’s MATH MAGIC: You can begin to see how the math provides a quantum-mechanical lens that elegantly integrates with my decentralized thesis. The equation quantifies the “why” behind DDW’s necessity in evolutionary biology: It’s the quantum enabler of high Probability transition, ensuring the DC electic trickle remains coherent for life’s exothermic symphony, with turnover as the reset valve. Disruptions (nnEMF, poor light) lower probability, favoring entropy over renewal.
The Fermi’s Golden Rule equation, below

This idea fits ideally into my decentralized, light-driven quantum biology thesis, because it provides a time-domain complement to the transition probability equation used for proteins alone. That equation is shown below.

The transition probability equation models how proteins (semiconductive entities in my framework) achieve functional activation through vibronic coupling and phase coherence, directly linking to the queries’ emphasis on DDW-enabled folding for electronic induction and the fate of DDW during mitochondrial turnover. From first principles, it underscores biology as a light-orchestrated quantum system where coherence determines energy flow efficiency, echoing GOE adaptations where oxygen and photons selected for precise electron-vibration interplay to mitigate entropy.
While the equation above described the instantaneous probability of a conformational switch (vibronic activation in proteins like the leptin receptor), Fermi’s Golden Rule gives the rate (probability per unit time) of irreversible quantum transitions between discrete or quasi-continuous states operates to perfectly capture how biology harnesses sunlight to drive coherent, high-rate electron and energy transfers in semiconductive proteins surrounded by DDW.
Core Integration with this Thesis
From first principles, biology post-GOE evolved as a quantum engine where oxygen-enabled exothermic reactions (ΔG << 0) must occur at precise rates to sustain the DC trickle, protein coherence, and metabolic flux without runaway entropy. Fermi’s Golden Rule quantifies this rate control:
- |\langle \psi_f | \hat{V} | \psi_i \rangle|^2 (Coupling Strength):
- This is the squared matrix element of the perturbation Hamiltonian \hat{V}
(light-induced electric field or vibronic interaction). - Directly analogous to |d_{ij}|^2 in the prior equation, it measures how strongly the initial electronic/vibrational state |\psi_i⟩ couples to the final state |\psi_f⟩.
- In my framework: Sunlight (UV-A/red-IR) acts as \hat{V}, exciting aromatic residues (L-tyrosine/tryptophan at ~280 nm) or heme in CCO (605 nm). DDW from functional CCO optimizes folding, aligning orbitals for large matrix elements which provide strong coupling yields high transition rates. Deuterium accumulation or nnEMF weakens |\langle \psi_f | \hat{V} | \psi_i \rangle|^2 (by disrupting geometry or coherence), slowing rates and collapsing the DC current, leading to misfolding and disease.
- ρ(E_f) (Density of Final States):
The number of available states at the final energy E_f.
Critical for biology’s efficiency: In dense bands (e.g., delocalized π-systems in folded proteins or mitochondrial cristae EZ water), ρ(E_f) is high, enabling rapid, near-unit-efficiency transfers (as in photosynthetic reaction centers or CCO’s electron funnel).
Ties to leptin-melanocortin: In leptin-sensitive states, tight mitochondrial coupling and high DDW create a quasi-continuous density of states for exothermic electron flow down the ETC (~400 mV to +800 mV gradient), maximizing W_{fi} for ATP production and heat. Hypoxia or CCO failure sparsens ρ(E_f) (band gaps widen), dropping rates because energy “escapes” inefficiently as aberrant UPEs or ROS, mirroring my exothermic “leak” concept.
- Overall Rate W_{fi} (Transitions per Second):
Determines the speed of life’s quantum processes: electron transfer in ETC (~10^{12}-10^{15} s⁻¹), proton tunneling, UPE emission, photorepair.
In healthy systems (proper sunlight, DDW): High W_{fi} sustains coherent DC trickle and exergonic dominance because fast rates capture energy before decoherence (τ ~ ps).
In disrupted systems (blue light, deuterium excess, polarized light): Low W_{fi} forces endergonic backups (e.g., glycolysis), senescence via HKDC1 overload, and leptin resistance (slow receptor activation).
Specific Ties to the thesis
DDW and Protein Folding: DDW minimizes zero-point energy broadening and vibrational damping, preserving large |V_{fi}| and dense ρ(E_f). CCO failure halts DDW production → reduced matrix elements → slower transitions → misfolded proteins can’t sustain high-rate electronic induction → DC current collapses.
Mitochondrial Turnover and Deuterium Excretion: Mitophagy (HKDC1 pathway) clears low-rate mitochondria (poor coupling/density), excreting deuterated water via sweat/urine to restore high W {fi} globally.
Exothermic Energy Flow and Leptin-Melanocortin: The ETC is a cascade of Fermi-governed transitions but each step exothermic but rate-limited by light-tuned coupling. Melatonin nocturnal uncoupling lowers W {fi} temporarily (endergonic repair phase), while morning red light spikes it for exergonic power.
Dopamine-Neuromelanin Paradox and Phase Coherence: Neuromelanin scaffold contains radical transitions; overload floods states, increasing ρ(E_f) pathologically → runaway rates → radical escape. Prior cos²(Δφ) modulates instantaneous probability, while Fermi adds the key temporal dimension and it provides coherent phase (Δφ ≈ 0) and it sustains high rates over time.
ρ(E_f) for Protein Activation: In the context of Fermi’s Golden Rule applied to eletronic protein activation within my decentralized thesis, ρ(E_f) represents the density of final quantum states available at the energy E_f of the activated conformation. For large biomolecules like proteins, this density arises from the quasi-continuous spectrum of vibrational, rotational, and conformational modes, often modeled as a phonon bath or vibronic continuum. Quantitatively, in quantum biological systems such as electron transfer in proteins or enzyme activation, ρ(E_f) can range from 10^3 to 10^6 states per eV, depending on the system’s degrees of freedom (e.g., 3N-6 modes for N atoms, leading to dense spectra in proteins with thousands of atoms). This high density ensures rapid transition rates (W_{fi} ~10^{10}-10^{15} s⁻¹) for efficient activation, as seen in light-driven processes like neuropsin or CCO excitation. In my decentralized model, DDW optimizes ρ(E_f) by sharpening energy levels (reducing broadening from isotope effects), while misfolding (e.g., from CCO failure) sparsens it, slowing rates and promoting entropy.
Quantitative Changes from DDW: Deuterium-depleted water (DDW, typically <100 ppm D vs. 150 ppm in normal water) quantitatively alters biological kinetics and thermodynamics via the kinetic isotope effect (KIE), where deuterium’s mass slows hydrogen-transfer reactions by a factor of 5-8 (enzyme catalysis rates increase 5-7x in DDW). This enhances proton tunneling probabilities (2-10x faster), reduces water viscosity by 20-25% (improving diffusion coefficients to 2.5 × 10^{-9} m²/s), and boosts mitochondrial efficiency (e.g., ATP yield up 10-30% via better ETC proton gradients). In cellular processes, DDW retards cancer cell proliferation (doubling time increases 20-50%), suppresses amoeboid movement in vitro (2-3x reduction), and shifts D/H ratios in tissues (e.g., 10-20% decrease after consumption), promoting adaptation and reducing ROS by 15-30%. In my thesis, this quantifies DDW’s role in enhancing protein folding (bond energies stabilize 5-10 kJ/mol), quantum coherence (coherence times extend 10-100 fs), and the DC trickle (current efficiency up ~20-50%), countering CCO failure’s entropy buildup.
Phase Coherence in the Formulation: Phase coherence enters Fermi’s Golden Rule implicitly through the matrix element |\langle \psi_f | \hat{V} | \psi_i \rangle|^2, which encodes wavefunction overlap and phase relationships between initial and final states—constructive interference (Δφ ≈ 0°) amplifies the coupling strength, while destructive phases (Δφ ≈ 90°-180°) suppress it. In quantum transitions, coherence modulates the effective perturbation \hat{V} ( light fields), enhancing rates in coherent regimes (e.g., vibronic coupling in proteins) but leading to breakdown in strongly coherent systems where FGR’s weak-coupling assumption fails. In my thesis formulation, it bridges to the prior P_transition via cos²(Δφ), where phase alignment (tuned by sunlight/DDW) boosts |V_{fi}|^2, ensuring high W_{fi} for coherent DC current; decoherence (e.g., deuterium damping) randomizes phases, reducing rates and favoring exothermic leaks as UPEs.
Evolutionary and Global Perspective
Post-GOE, oxygen demanded ultra-fast transition rates to outpace ROS damage and Fermi’s rule selected for high |V_{fi}| (for L-aromatic/heme systems) and dense ρ(E_f) (delocalized proteins in DDW).
My thesis globalizes this idea: Every protein transition from leptin receptor phosphorylation to CCO oxygen reduction is Fermi-rate-limited, with sunlight as the universal perturbation \hat{V}. For example, why did I post all those Kreb’s bicycle blogs? To show you how covalent succination involves the addition of succinate (from TCA cycle intermediates) to cysteine thiols in proteins, forming a thioether-like bond (~200-300 kJ/mol bond energy). This modification disrupts protein function, increases ROS, and promotes metabolic chaos (in fumarate hydratase-deficient cancers), amplifying entropy (ΔS > 0) and decohering the DC electric trickle.
My thesis posits biology as a light-orchestrated semiconductor network, where sunlight’s photons (E = hc/λ) excite electrons to break such bonds via non-adiabatic transitions, without enzymatic intermediaries which is much like how hypoxia degrades melanin to dopamine precursors but light restores balance. That is why this slide has been shown 1000 times in my blogs. You may not have understood its significance but you should now.

LIFE EXISTS ON A SMALL TRICKLE OF DC CURRENT TRANSFORMED FROM SUNLIGHT
The “trickle” of the DC current Becker found is the macroscopic sum of these microscopic rates; coherence (via heme proteins creation of DDW, followed by UV light) keeps W {fi} optimal, balancing exothermic release with quantum control.In essence, Fermi’s Golden Rule is the kinetic engine of my model and it explains not just if a transition happens (prior probability), but how fast and efficiently, making biology a sunlight-orchestrated quantum rate machine since the oxygenation of Earth.
In this blog I tied this idea to the exothermic infographic and the ETC/sun exposure graph above.
Biology favors exergonic (spontaneous, energy-releasing, ΔG < 0) flows under red light, think ETC electron cascades releasing 200 kJ/mol per O₂ at CCO—but full spectrum sunlight tunes in the endergonic (energy-input) phases for repair and coherence.
The graphs above illustrates this: Active sun exposure optimizes the redox potential gradient (-400 mV at NADH to +800 mV at O₂), enhancing survival by maintaining proton tunneling and reducing ROS waste.
Avoiding sun flattens efficiency, mimicking senescence. In my thesis, this “trickle of electricity” which is akin to Becker’s current of injury, 0.5–10 µA/cm², triggers regeneration and determines directionality of repair using triplet state nitric oxide as the second messenger.
Coherent under DDW (faster kinetics, 5–10 kJ/mol stronger H-bonds, diffusion 2.3 × 10^{-9} m²/s), it powers exergonic dominance; decoherent (deuterium buildup slows tunneling 7-fold via kinetic isotope effects) , it forces endergonic compensations, spiking entropy which leads to heteroplasmy and disease.
SUMMARY
Leptin-Melanocortin Pathway evoled to be Net Exergonic, with Light-Gated Endergonic Reversals
This analysis nails Nick lane’s question we started with.

It appears evolution favors systems that minimize entropy while maximizing information extraction from chaos (environmental waves). The leptin-melanocortin pathway mirrors mitoception’s need for singlet/triplet feedback: Singlets (short-lived, dissipative radicals) signal ancestral “burning” modes (high-entropy glycolysis), while triplets (metastable, coherent) enable “processing” for complexity (magnetic reservoirs via spin S=1). The brain, via its hypothalamic POMC neurons, “feels” this status through:
Photonic/UPE Signals: Mitochondria emit UPE (10^{-18} W/cm², UV-IR range) as de Broglie waves of excited electrons/protons, guided by Bohmian pilots for non-local coherence. Leptin relays adipose-derived energy audits, but mitoception added quantum layers to the feedback loop because GDF15 surges (2-5x in stress) as a molecular proxy for triplet depletion, prompting α-MSH to redistribute melanin (a broadband absorber/conductor) for field buffering.
Electromagnetic Resonance: Mitochondria sense polarized light/nnEMF via heme/iron chromophores, where de Broglie wavelengths (pm for protons) resonate with matrix confinement (nm scales), enabling pilot-wave interference. Disruption of electromagnetic resonance via polarization elevates GDF15, signaling “energy failure” to the pathway, which then mobilizes melanin along ancient neuroectodermal migration routes (neural crest derivatives), recalibrating thermodynamic “zipcodes” (tissue-specific redox potentials).
This leptin accountant role evolved post-K-T event (~66 Ma), where light-sensitive POMC adaptations (seasonal melanin shifts) allowed survival in variable fields, rising to critical importance in humans because it built frontal lobe complexity through this coherent feedback loop.
For example, in melanin-iron complexes in the eye or skin, blue light alters electron spin (via SOC), broadening NIR absorption and intensifying oxidative damage. This disrupts redox fields, as Fe²⁺-catalyzed Fenton reactions spike ROS, feeding back to leptin-melanocortin for systemic accounting by elevated GDF15 correlates with mitochondrial uncoupling and entropy rise.
Parity Violation Link: Weak force parity violation (non-mirror symmetry in beta decay, 10^{-6} energy scale) biases L-amino acids over D amino acids in biology. The leptin melanocortin pathway relies critically on aromatic amino acids to absorb light. Blue light’s polarized photons (circular/elliptical) interact with chiral melanin (helical structure), amplifying local asymmetries via spin-polarized electrons (de Broglie waves with handedness). In α-MSH-expressing regions of the body (UV-stimulated POMC cleavage), UPE (380-450 nm) should flip isomer ratios if L-substrates are scarce, losing feedback by causing D-enrichment of amino acids and this disrupts enzyme kinetics (KIE-like), eroding coherence in tissues which leads to disease. This paper supports this indirectly: Melanin’s metal chelation mitigates but amplifies under light stress, tying it to thermodynamic zipcodes where parity-violating weak interactions (in heme) influence radical lifetimes.
Without L-amino acids, the system loses chiral control, reverting to high-entropy state which ruins the energy feedback loop causing endogenous breakdown.
This pathway (leptin from adipocytes signals ARC neurons, activating POMC/α-MSH for MC4R to curb appetite/boost expenditure) handles mitochondrial energy as a net exergonic engine. This pathways gave us the ability to oxidize fuels to release heat/ATP (ΔH < 0), but the oxidation state of iron toggles endergonic potential to allow for adaptation.
Exergonic dominance: Leptin boosts OXPHOS in BAT (UCP1 uncoupling, RQ ~0.7), and evolution put melanin close so that the exothermic ROS could be contained by neuromelanin in brain which became more complex since the last extinction event.
Endergonic flips occur daily in darkness with temperature drops in the hypothalmus. How do we know this is accurate? Nighttime melatonin reverses ETC slightly for NAD⁺ buildup; hypoxia invests in Warburg glycolysis (ΔG > 0 locally). Sunlight (red/IR) enhances CCO for efficient exergonic flow; UV-A invests in repair. Polarized light and nootropics disrupting HKDC1 and tip the entire leptin melanocoritcal pathway toward wasteful endergonic consumption, creation of singlet state radicals, while killing coherence faster in tissues simultaneously, and it is why I do not recommend polarized light and/or supplements.
CITES
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0375960117303389